Vitamin A in Skincare: The Different Types Explained
Vitamin A is one of the most researched and results-driven ingredients in professional skincare.
From acne and pigmentation to ageing and skin texture, it plays a critical role in skin health and regeneration.
However, not all Vitamin A is the same.
In this blog, we break down the different types of Vitamin A used in skincare, how they work, and who they’re best suited for — so both beauty professionals and consumers can make informed choices.
What Is Vitamin A and Why Is It Used in Skincare?
Vitamin A is a cell-communicating ingredient that works by influencing how skin cells behave. It helps to:
Increase cell turnover
Stimulate collagen production
Improve acne and congestion
Reduce pigmentation and sun damage
Smooth fine lines and uneven texture
In skincare, Vitamin A is typically referred to as retinoids, a family of compounds derived from Vitamin A.
The Vitamin A Conversion Pathway (Why Strength Matters)
Most Vitamin A types must be converted by the skin into Retinoic Acid (the active form).
The more conversion steps required, the gentler the product — but also slower the results.
More conversion = gentler
Less conversion = stronger
1. Retinyl Esters (Retinyl Palmitate, Retinyl Acetate)
Best for: Sensitive skins, beginners, maintenance routines
What it is?
Retinyl esters are the mildest form of Vitamin A used in skincare. They must go through three conversion steps in the skin before becoming active.
Benefits
Improves skin texture gradually
Supports barrier function
Minimal irritation risk
Considerations
Results are subtle and slow
Not ideal for treating advanced acne or ageing concerns
Therapist tip: Ideal as an entry-level Vitamin A or for clients unable to tolerate stronger actives.
2. Retinol
Best for: Ageing, pigmentation, acne-prone skins (non-sensitive)
What it is
Retinol is the most widely recognised Vitamin A and sits in the mid-strength category. It requires two conversion steps to become active.
Benefits
Boosts collagen and elastin
Improves fine lines and uneven tone
Helps regulate oil and congestion
Considerations
Can cause dryness, peeling, or sensitivity
Requires careful introduction and sun protection
Therapist tip: Best introduced gradually with a structured homecare plan.
3. Retinal (Retinaldehyde)
Best for: Acne, ageing, pigmentation with faster results
What it is
Retinal is one conversion step away from Retinoic Acid, making it significantly more potent than retinol — but often better tolerated.
Benefits
Faster visible results
Strong antibacterial action (excellent for acne)
Improves texture and tone
Considerations
Still requires professional guidance
Can cause irritation if overused
Therapist tip: A strong option for clients who have already built tolerance to retinol.
4. Retinoic Acid (Tretinoin)
Best for: Medical skin conditions, severe acne, advanced ageing
What it is
Retinoic Acid is the active form of Vitamin A and does not require conversion. It is prescription-only in most countries.
Benefits
Fastest and most dramatic results
Clinically proven for acne and photoageing
Considerations
High irritation potential
Not suitable for sensitive skins
Requires medical supervision
Therapist note: This is a medical treatment, not a cosmetic one.
5. Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR / Granactive Retinoid)
Best for: Sensitive skins wanting results without irritation
What it is
HPR is a new-generation Vitamin A that binds directly to retinoid receptors without full conversion.
Benefits
Low irritation profile
Suitable for sensitive and reactive skins
Good anti-ageing support
Considerations
Long-term clinical data is still emerging
Results may be slower than retinal or retinoic acid
Therapist tip: Ideal for clients who “can’t tolerate retinol” but still want Vitamin A benefits.
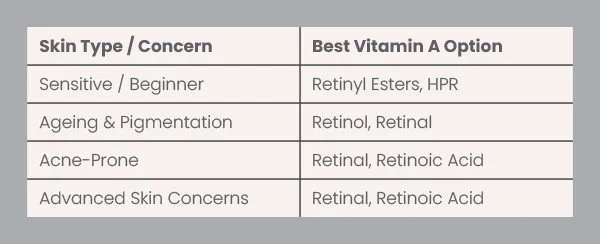
Which Vitamin A Is Best?
There is no single “best” Vitamin A — only the right one for the skin condition, tolerance level, and treatment goals.
Important Vitamin A Safety Notes
Always introduce Vitamin A slowly
Night-time use only (unless professionally formulated otherwise)
Daily SPF is essential
Not recommended during pregnancy (unless medically approved)
Final Thoughts
Vitamin A remains the gold standard ingredient in professional skincare — but understanding the type, strength, and delivery system is critical for achieving results without compromising skin health.
For therapists, education ensures correct prescribing.
For consumers, knowledge prevents misuse and irritation.
When used correctly, Vitamin A can truly transform the skin.